3D Printers: How Layer‑by‑Layer Innovation Is Shaping the Future
3D printers are revolutionizing manufacturing by turning digital designs into physical objects, layer by layer. From rapid prototyping to custom medical devices, this technology allows industries to create complex, precise items faster, with less waste, and opens new possibilities in engineering, art, and healthcare.
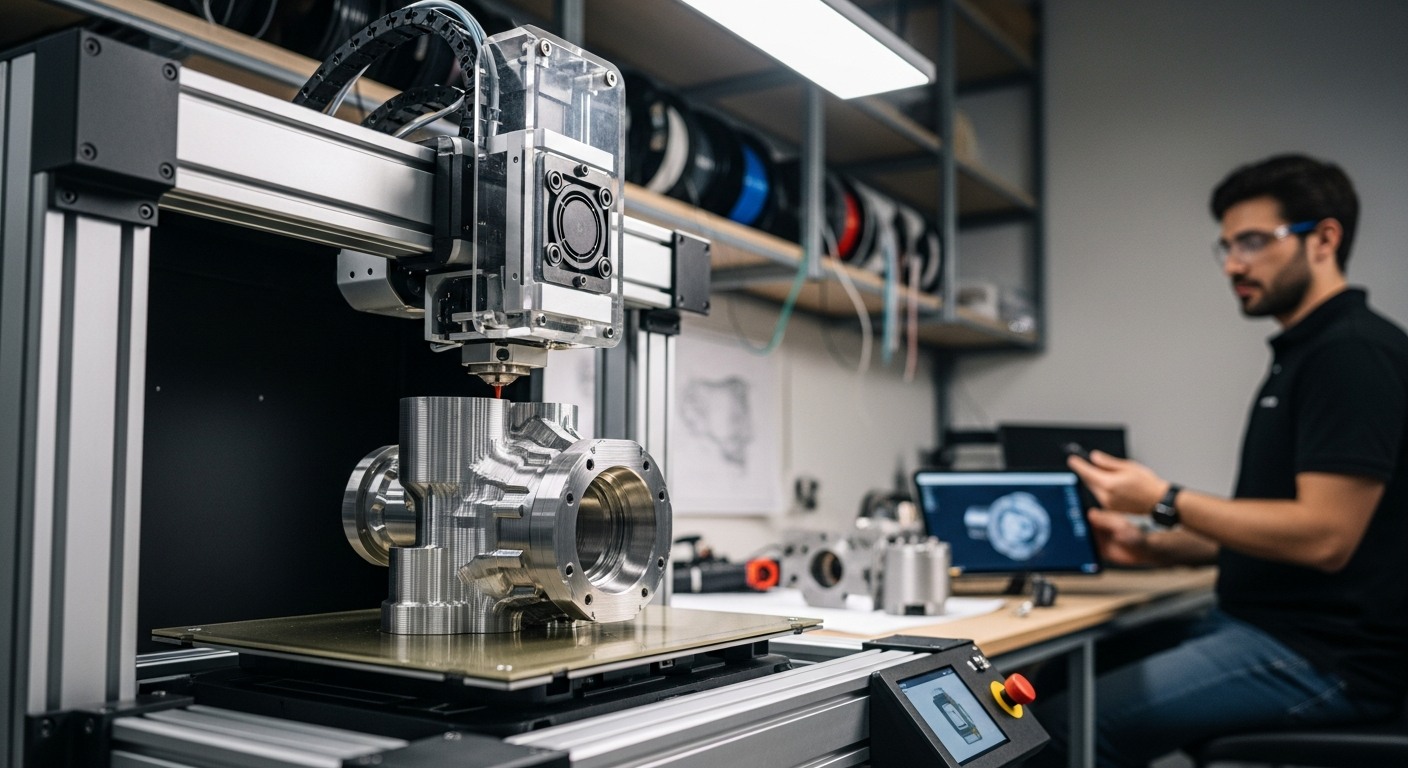

How Additive Manufacturing Transforms Digital Designs into Physical Objects
Additive manufacturing processes turn digital designs into real objects layer by layer. The fundamental principle involves taking a digital 3D model, typically created with Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, and slicing it into hundreds or thousands of thin horizontal layers. Each layer is then precisely recreated by the printing system, usually by depositing, curing, or fusing material in a specific pattern. This additive approach builds the object from the ground up, one cross-section at a time, until the final three-dimensional form is achieved. Common materials used include plastics, resins, metals, and even ceramics, each requiring different printing technologies such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), or Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
Diverse Applications Across Medicine, Engineering, and Art
This technology is used in fields like medicine, engineering, and art, showcasing its remarkable versatility. In medicine, additive manufacturing facilitates the creation of custom prosthetics, surgical guides, and even bioprinted tissues and organs for research. Engineers utilize it for rapid prototyping, creating complex parts with intricate geometries that are difficult or impossible to produce with conventional methods, and for producing functional end-use components. Artists and designers employ it to realize complex sculptures, intricate jewelry, and unique architectural models, pushing the boundaries of creative expression and material exploration. The aerospace and automotive industries also leverage additive manufacturing for lightweight, high-performance parts, contributing to fuel efficiency and advanced design.
The Role of Additive Manufacturing in Rapid Prototyping
Additive manufacturing makes rapid prototyping faster and more affordable, significantly impacting product development cycles. Traditionally, creating physical prototypes could be a lengthy and expensive process involving specialized tooling and skilled labor. With additive manufacturing, designers and engineers can quickly iterate on designs, producing multiple versions of a prototype in a matter of hours or days, rather than weeks. This accelerated feedback loop allows for faster identification of design flaws, more efficient testing, and quicker refinement before committing to mass production. The ability to produce functional prototypes on demand reduces both the time to market and the overall costs associated with product development.
Understanding the cost implications of additive manufacturing systems is crucial for potential users, ranging from hobbyists to industrial manufacturers. Prices vary significantly based on the technology, build volume, material compatibility, and precision of the system. Entry-level FDM systems for home use can be relatively inexpensive, while professional-grade SLA or industrial metal additive manufacturing systems represent a substantial investment. Consumable materials like filament or resin also contribute to the ongoing operational costs, with specialized materials often being more expensive. Service bureaus offer another option, allowing access to high-end manufacturing without the upfront capital expenditure.
| Product/Service Name | Provider | Key Features | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ender 3 V3 SE | Creality | Entry-level FDM, auto-leveling, fast printing | $180 - $250 |
| Prusa i3 MK4 | Prusa Research | High-quality FDM, open source, reliable | $1,000 - $1,200 |
| Form 3+ | Formlabs | Desktop SLA, high resolution, diverse resins | $2,500 - $4,000 |
| Xact Metal XM200G | Xact Metal | Industrial metal additive manufacturing, powder bed fusion | $100,000 - $150,000 |
| Additive Manufacturing Service | Shapeways | On-demand manufacturing, various materials & technologies | Varies by project |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
In conclusion, additive manufacturing technology is continuously evolving, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in design and production. Its ability to create complex objects layer by layer from digital models has revolutionized prototyping, enabled customized solutions across diverse sectors, and offered new avenues for innovation. As materials and manufacturing processes become more sophisticated and accessible, additive manufacturing is set to play an even more integral role in shaping future industries and daily life.