3D Printing: Turning Imagination Into Reality
3D printing is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a hands-on tool that’s reshaping industries and creativity alike. Whether you’re a hobbyist crafting custom figurines or a company producing complex prototypes, the right 3D printer can make ideas tangible in hours instead of weeks. This article dives into cutting-edge printing technologies, practical applications, material choices, and expert tips to help you get the most out of your 3D printing experience.
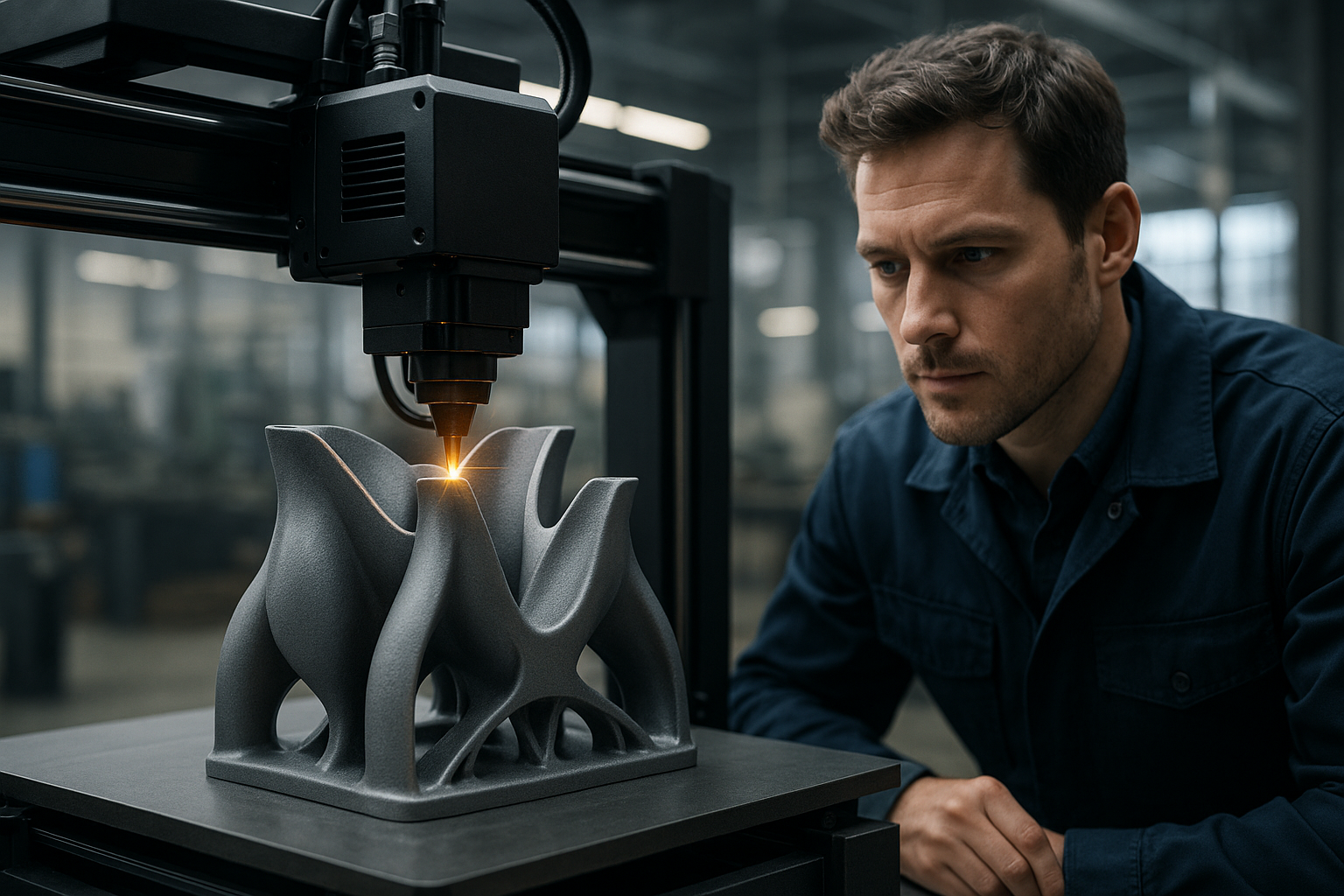

3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, builds objects by depositing material layer upon layer based on digital models. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing that cuts away material, this approach adds material only where needed, reducing waste and enabling intricate designs that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive with conventional methods. The process begins with a 3D model created using computer-aided design software, which is then sliced into thin horizontal layers. The printer reads these instructions and deposits material—plastic, resin, metal, or even biological substances—to construct the object from the ground up.
How Does High-Precision 3D Printing Work?
High-precision 3D printing relies on advanced technologies to achieve exceptional detail and accuracy. Methods like stereolithography use ultraviolet lasers to cure liquid resin into solid layers with resolutions as fine as 25 microns. Selective laser sintering fuses powdered materials using high-powered lasers, creating durable parts suitable for functional testing and end-use applications. Fused deposition modeling, the most common consumer method, extrudes thermoplastic filaments through heated nozzles, offering a balance between cost and quality. Precision depends on factors including layer height, nozzle diameter, calibration accuracy, and material properties. Industrial-grade machines achieve tolerances within hundredths of a millimeter, making them suitable for aerospace components, medical implants, and precision tooling.
What Makes 3D Printing Fast, Affordable, and Customizable?
Speed in 3D printing comes from eliminating traditional manufacturing steps like mold creation, machining setups, and assembly lines. A prototype that once took weeks can now be produced overnight. Affordability stems from reduced material waste, lower labor costs, and the elimination of expensive tooling. Desktop printers now start at a few hundred dollars, while materials like PLA filament cost as little as 20 dollars per kilogram. Customization is perhaps the greatest advantage—each printed object can be unique without additional cost. Medical professionals create patient-specific surgical guides, jewelers produce one-of-a-kind designs, and manufacturers offer personalized consumer products. This flexibility transforms business models, enabling on-demand production and mass customization previously unimaginable.
How Does Additive Manufacturing Transform Prototypes Into Products?
Additive manufacturing bridges the gap between concept and final product by enabling rapid iteration and functional testing. Designers create initial prototypes quickly, test them in real-world conditions, refine the design based on feedback, and produce updated versions within days. This accelerated development cycle reduces time-to-market and lowers development costs significantly. Beyond prototyping, 3D printing increasingly produces end-use parts. Aerospace companies print lightweight structural components, automotive manufacturers create custom interior elements, and medical device makers produce FDA-approved implants. The technology supports complex geometries like internal channels for cooling, lattice structures for weight reduction, and consolidated assemblies that replace multiple parts, improving performance while simplifying supply chains.
What Industries Benefit Most From 3D Printing Technology?
Healthcare leads adoption with custom prosthetics, dental aligners, surgical models, and bioprinted tissues. Aerospace and defense utilize lightweight, high-strength components that reduce fuel consumption and improve performance. Automotive manufacturers prototype new designs and produce limited-run parts for classic car restoration. Architecture and construction firms create detailed scale models and experiment with printing entire building structures. Education institutions use printers to teach design thinking and engineering principles. Consumer goods companies offer personalized products from footwear to eyewear. Even food and fashion industries explore 3D printing for customized nutrition and avant-garde designs. The versatility across sectors demonstrates the technology’s transformative potential.
What Are Real-World Cost Considerations for 3D Printing?
Costs vary widely based on printer type, material choice, and production volume. Entry-level desktop printers suitable for hobbyists and small businesses range from 200 to 1,000 dollars, with materials costing 20 to 50 dollars per kilogram. Professional-grade machines for engineering and product development typically cost 5,000 to 50,000 dollars, using specialized materials priced between 100 and 500 dollars per kilogram. Industrial systems for metal printing or large-scale production can exceed 500,000 dollars, with materials and maintenance adding substantial ongoing expenses. Service bureaus offer printing without equipment investment, charging based on material volume, complexity, and finish quality—typically ranging from 5 to 100 dollars per part depending on specifications.
| Printer Category | Typical Price Range | Material Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level Desktop | 200 - 1,000 dollars | 20 - 50 dollars/kg | Hobbyists, education, simple prototypes |
| Professional Desktop | 2,000 - 10,000 dollars | 50 - 150 dollars/kg | Small businesses, detailed prototypes |
| Industrial Resin/SLS | 20,000 - 100,000 dollars | 100 - 300 dollars/kg | Engineering, medical devices, production |
| Metal Printing Systems | 100,000 - 500,000+ dollars | 300 - 800 dollars/kg | Aerospace, automotive, high-performance parts |
| Service Bureau Printing | 5 - 100+ dollars/part | Included in service | One-off parts, testing without investment |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
What Should You Consider Before Investing in 3D Printing?
Before purchasing equipment or committing to 3D printing projects, evaluate your specific needs and constraints. Consider the size of objects you need to produce, as build volumes range from palm-sized to room-sized. Material requirements matter—some applications demand engineering-grade plastics, metals, or flexible elastomers, each requiring different printer technologies. Assess your technical expertise, as some systems require significant calibration and maintenance knowledge. Factor in total cost of ownership including materials, replacement parts, software licenses, and training. Determine whether in-house printing or outsourcing to service providers better suits your volume and timeline. Review post-processing requirements, as many prints need support removal, sanding, painting, or curing. Understanding these factors ensures realistic expectations and successful implementation.
3D printing continues evolving rapidly, with improvements in speed, material properties, and accessibility expanding its applications daily. Whether you are an entrepreneur developing new products, an educator inspiring students, or a hobbyist exploring creative possibilities, this technology offers unprecedented opportunities to turn imagination into tangible reality. As costs decrease and capabilities increase, 3D printing moves from specialized tool to mainstream manufacturing method, reshaping how we design, produce, and interact with physical objects in virtually every industry and aspect of daily life.