Confidential and Accurate HIV Testing Solutions
HIV tests are designed to deliver accurate and timely results in a confidential manner. Suitable for use in home or clinical environments, these tests are easy to administer and provide reliable information to support informed health decisions. Fast and discreet testing helps promote awareness and proactive health management.
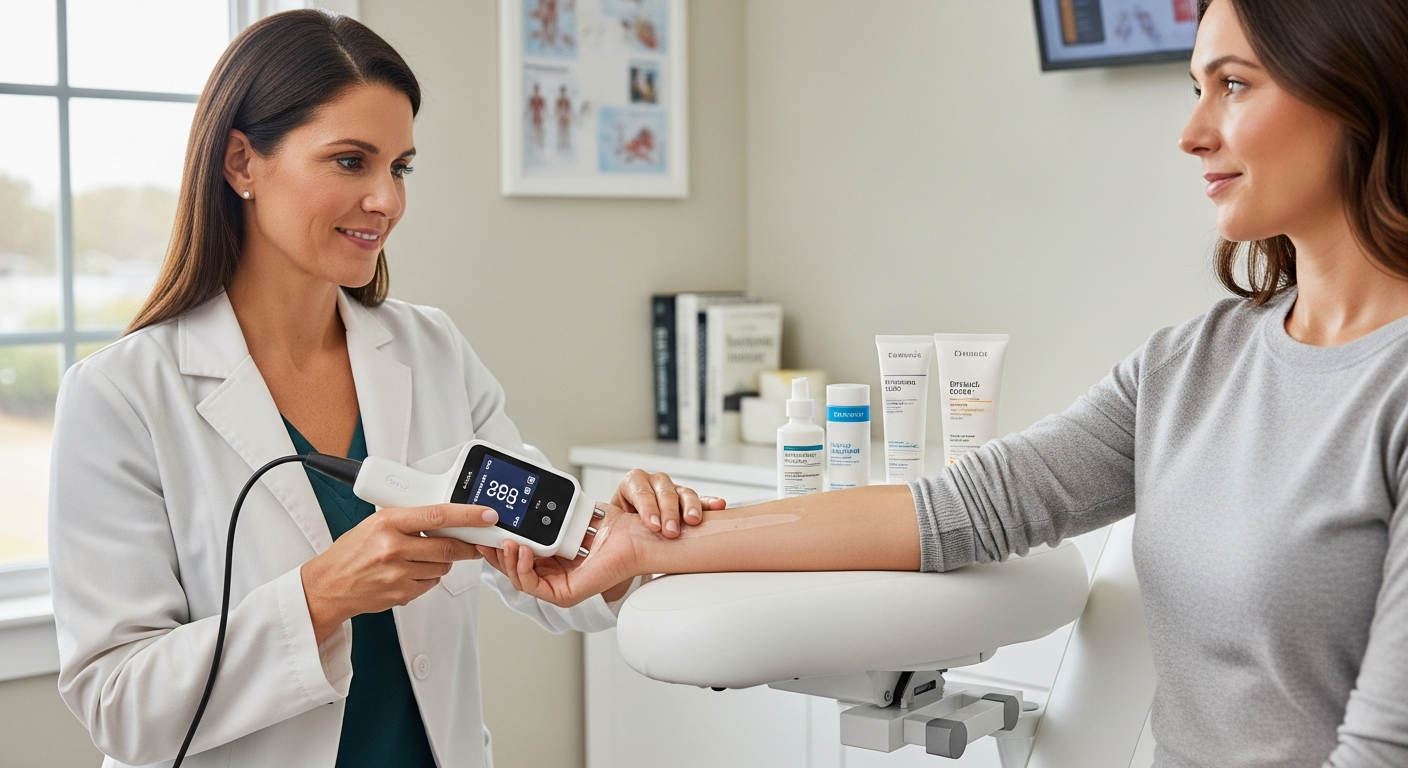

Fast and Reliable HIV Screening Methods
Modern HIV screening encompasses several testing approaches, each designed to detect the presence of HIV antibodies or antigens in the body. The most common methods include antibody tests, antigen/antibody combination tests, and nucleic acid tests (NAT). Antibody tests detect proteins produced by the immune system in response to HIV infection, typically becoming detectable 23 to 90 days after exposure. Antigen/antibody combination tests can identify both HIV antibodies and p24 antigens, reducing the window period to 18 to 45 days after exposure.
Rapid testing options provide results within 20 minutes, making them valuable for immediate screening needs. These tests use blood from a finger stick or oral fluid samples, offering convenience without compromising accuracy. Laboratory-based tests generally provide the highest accuracy levels and serve as confirmatory testing when rapid tests show reactive results.
Confidential Testing with Accurate Results
Confidentiality remains a cornerstone of HIV testing services, with healthcare providers bound by strict privacy regulations. Anonymous testing options allow individuals to receive testing without providing personal identifying information, using only a unique number or code for result retrieval. Confidential testing maintains privacy while creating a medical record that healthcare providers can access for follow-up care.
Accuracy rates for modern HIV tests exceed 99% when performed correctly and within appropriate timeframes. False positive results are rare but may occur, necessitating confirmatory testing through additional methods. False negative results typically happen when testing occurs during the window period before antibodies or antigens reach detectable levels.
Testing facilities implement quality control measures including regular calibration of equipment, staff training programs, and participation in proficiency testing programs to maintain accuracy standards.
Simple HIV Testing for Informed Decisions
The testing process has been streamlined to reduce barriers and encourage regular screening. Most tests require minimal preparation, with no fasting or special dietary restrictions necessary. Pre-test counseling helps individuals understand the testing process, window periods, and result interpretation.
Home testing kits approved by regulatory agencies provide another option for those preferring privacy or facing access barriers. These kits include detailed instructions and connect users with counseling services for result interpretation and next steps. However, reactive home test results require confirmatory testing through healthcare providers.
Post-test counseling addresses result interpretation, prevention strategies, and connection to appropriate care services. For negative results, counseling covers risk reduction strategies and recommendations for future testing frequency based on individual risk factors.
| Testing Method | Provider Type | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Blood Test | Community Health Centers | $25 - $60 |
| Laboratory Antibody Test | Private Clinics | $50 - $150 |
| Home Test Kit | Pharmacy/Online | $40 - $80 |
| Combination Test | Hospital Labs | $75 - $200 |
| Anonymous Testing | Public Health Departments | Free - $30 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Understanding Test Results and Next Steps
Test results fall into three categories: negative, positive, or indeterminate. Negative results indicate no HIV antibodies or antigens were detected at the time of testing. However, testing during the window period may produce false negative results, making retesting necessary if recent exposure occurred.
Positive or reactive results require immediate confirmatory testing using different methods. Initial positive results do not definitively confirm HIV infection, as false positives can occur. Confirmatory testing typically involves more sophisticated laboratory techniques with higher specificity.
Indeterminate results occur when test findings are unclear or borderline. These situations require additional testing and consultation with healthcare providers to determine appropriate next steps.
Accessing Testing Services and Support
Testing services are available through various channels including community health centers, private healthcare providers, specialized testing clinics, and mobile testing units. Many locations offer walk-in services without appointments, reducing access barriers.
Insurance coverage varies by provider and plan type, with many policies covering routine HIV screening as preventive care. Uninsured individuals can access testing through federally qualified health centers, public health departments, and community-based organizations offering free or sliding-scale fee services.
Support services accompanying testing include pre- and post-test counseling, linkage to care for positive results, and prevention education. Many facilities provide multilingual services and culturally competent care to serve diverse populations.
Regular HIV testing forms an essential component of comprehensive healthcare, particularly for individuals with increased risk factors. Understanding available testing options, accuracy considerations, and support services enables informed decision-making about personal health management. Confidential and accurate testing solutions continue expanding accessibility while maintaining the privacy and quality standards essential for effective HIV prevention and care programs.