Modern Hearing Aids in the U.S.: What Seniors Should Know Before Choosing One
Hearing loss affects millions of seniors across the United States, impacting communication, social engagement, and overall quality of life. With advancements in technology, today's hearing devices offer features that were unimaginable just a decade ago. Understanding the options available, how they function, and what to consider before making a purchase can help seniors make informed decisions that best suit their lifestyle and budget.
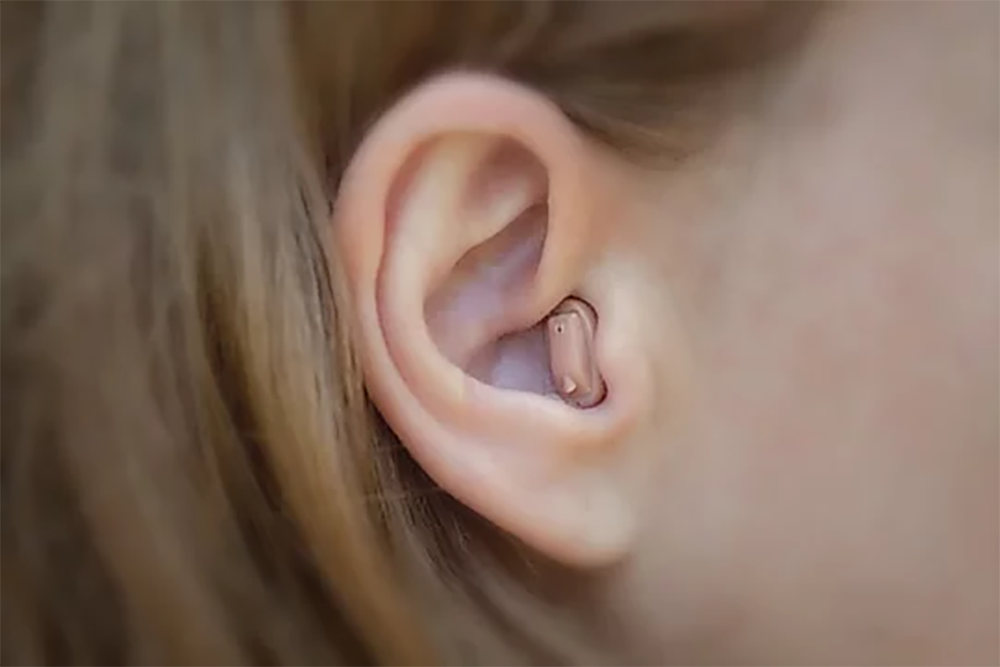
As we age, hearing loss becomes increasingly common, affecting approximately one in three adults over 65 in the United States. Modern hearing technology has evolved significantly, offering solutions that are smaller, more powerful, and equipped with features like Bluetooth connectivity and rechargeable batteries. For seniors navigating this landscape, understanding the fundamentals of hearing devices, the differences between product types, and the importance of professional guidance can make all the difference in selecting the right solution.
What Are Hearing Aids and How Do They Work?
Hearing aids are small electronic devices designed to amplify sound for individuals with hearing loss. They consist of three main components: a microphone that picks up sound from the environment, an amplifier that increases the sound’s volume, and a speaker that delivers the amplified sound into the ear canal. Modern devices use digital technology to process sound, allowing for customization based on the user’s specific hearing loss pattern. Digital hearing aids can distinguish between speech and background noise, adjust volume automatically, and even connect wirelessly to smartphones and televisions. The sophistication of these devices means they can be programmed to address mild to profound hearing loss, with settings tailored to different listening environments such as quiet rooms, restaurants, or outdoor spaces.
Hearing Aids vs. Hearing Buds: What’s the Difference?
The market now includes both traditional hearing aids and newer products called hearing buds or personal sound amplification products. Traditional hearing aids are medical devices regulated by the FDA, designed specifically to treat diagnosed hearing loss. They are customized based on a hearing test and programmed by a licensed audiologist or hearing instrument specialist. Hearing buds, on the other hand, are often marketed as over-the-counter devices intended for people with mild to moderate hearing loss. While they may look similar to earbuds and cost less, they typically lack the customization and advanced features of prescription hearing aids. The FDA introduced a category of over-the-counter hearing aids in 2022, providing a middle ground for adults with perceived mild to moderate hearing loss who want an accessible option without a prescription. However, these devices may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with more severe hearing loss or specific medical conditions affecting the ear.
Why Professional Fitting Matters
While over-the-counter options have expanded access to hearing assistance, professional fitting remains crucial for optimal results. An audiologist or hearing specialist conducts comprehensive hearing tests to determine the type and degree of hearing loss, which can vary significantly between individuals. This assessment identifies whether hearing loss is due to age-related changes, noise exposure, medical conditions, or other factors. Professional fitting ensures that devices are programmed precisely to match the user’s hearing profile, maximizing both clarity and comfort. Audiologists also provide ongoing support, including adjustments as hearing changes over time, troubleshooting technical issues, and counseling on realistic expectations. Improperly fitted devices can lead to discomfort, feedback issues, or inadequate amplification, potentially discouraging users from wearing them consistently. For seniors with complex hearing needs or those new to hearing devices, professional guidance significantly improves the likelihood of successful adaptation and long-term satisfaction.
Average Hearing Aid Prices in the U.S. (2025)
The cost of hearing aids varies widely depending on technology level, features, and whether professional services are included. Understanding the price landscape helps seniors budget appropriately and explore available options. Entry-level devices typically offer basic amplification with fewer customization options, while premium models include advanced features like directional microphones, noise reduction algorithms, and wireless connectivity.
| Device Type | Provider Examples | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids | Sony, Jabra Enhance, Lexie | $200 - $1,000 per pair |
| Mid-Range Prescription Hearing Aids | Costco Hearing Aid Centers, Sam’s Club | $1,400 - $2,800 per pair |
| Premium Prescription Hearing Aids | Phonak, Oticon, Widex, Signia | $2,500 - $7,000 per pair |
| Online Hearing Aid Services | Eargo, Audicus, hear.com | $1,000 - $3,000 per pair |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Most prescription hearing aid prices include professional services such as fitting, follow-up adjustments, and warranty coverage. Some providers offer financing options or payment plans to make devices more affordable. Medicare does not typically cover hearing aids, though some Medicare Advantage plans may offer partial coverage. Veterans may qualify for hearing aids through the VA at reduced or no cost. Many states have programs to assist low-income seniors with hearing device expenses.
Additional Considerations for Seniors
Beyond cost and technology, seniors should consider factors like ease of use, battery type, and maintenance requirements. Rechargeable hearing aids eliminate the need to handle small batteries, which can be challenging for those with dexterity issues. Device size matters too—while smaller aids are less visible, they may be harder to manipulate and have shorter battery life. Lifestyle plays a role in selection: active individuals who frequently attend social events may benefit from devices with advanced noise management, while those who primarily stay at home might find simpler models sufficient. Trial periods are common in the industry, allowing users to test devices in real-world situations before committing to a purchase. Seniors should ask about return policies, warranty coverage, and what services are included in the price. Reading reviews and seeking recommendations from others who use hearing aids can provide valuable insights into product performance and customer service quality.
Moving Forward with Confidence
Choosing a hearing aid is a significant decision that impacts daily communication and quality of life. Seniors should start by getting a comprehensive hearing evaluation from a licensed professional, even if considering over-the-counter options. This assessment provides a baseline understanding of hearing health and helps identify any underlying medical issues that require attention. Comparing multiple providers and product options ensures finding a solution that balances features, comfort, and budget. Many audiologists offer consultations to discuss needs and demonstrate different devices. Taking advantage of trial periods allows for testing in various environments before making a final decision. With the right information and professional support, seniors can find hearing solutions that help them stay connected to the people and activities they value most.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.