Noticing a Lump Under Your Skin? Here’s What It Might Mean
Finding an unexpected lump under your skin can be concerning, but most skin lumps are harmless and have simple explanations. These growths can appear anywhere on the body and vary significantly in size, texture, and cause. While some lumps develop gradually over time, others may appear suddenly, leading to natural worry about their significance. Understanding the various types of skin lumps, their common causes, and knowing when professional medical evaluation is necessary can help ease anxiety and ensure appropriate care when needed.
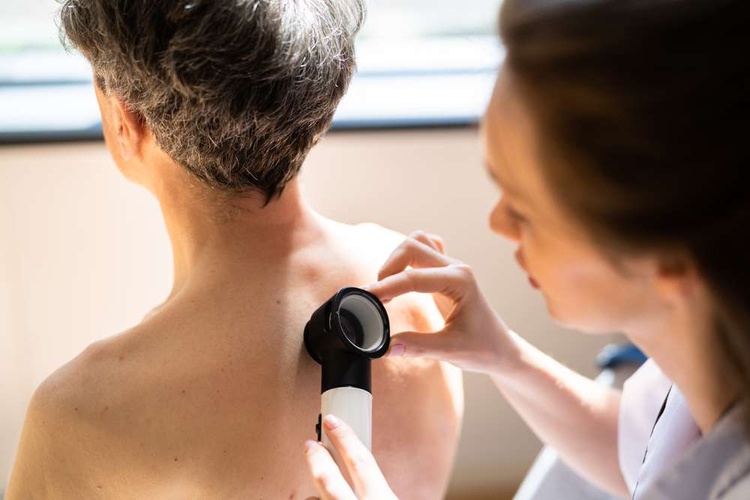
Skin lumps are incredibly common and affect people of all ages. These growths can range from tiny, barely noticeable bumps to larger, more prominent masses that develop beneath the skin’s surface. Most skin lumps are benign, meaning they’re not cancerous or dangerous, but understanding their characteristics and potential causes helps determine the appropriate response.
Understanding the Common Causes of Skin Lumps
Several factors contribute to lump formation under the skin. Lipomas represent one of the most frequent types, consisting of soft, fatty tissue that moves easily when touched. These growths typically develop slowly and feel rubbery or doughy. Sebaceous cysts form when oil glands become blocked, creating fluid-filled sacs that may feel firm or tender. Lymph nodes can also swell due to infections or immune responses, creating temporary lumps in areas like the neck, armpits, or groin.
Other common causes include ingrown hairs, which create small, sometimes painful bumps, particularly in areas where hair is regularly shaved or waxed. Fibromas are benign growths of fibrous tissue that feel firm and may develop after injury or irritation. Muscle knots or trigger points can also create the sensation of lumps, especially in areas prone to tension like the shoulders or back.
What Causes a Lump to Appear?
Lump formation occurs through various mechanisms depending on the underlying cause. Genetic predisposition plays a role in some cases, particularly with lipomas, which often run in families. Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can trigger the development of certain types of lumps. Trauma or injury to the skin may lead to scar tissue formation or trigger the body’s healing response, resulting in firm lumps.
Infections, whether bacterial, viral, or fungal, commonly cause temporary swelling and lump formation as the immune system responds. Poor hygiene, tight clothing, or friction from repetitive activities can contribute to blocked pores and subsequent cyst formation. Age-related changes in skin elasticity and cellular turnover may also increase the likelihood of developing various types of skin growths.
When Should You See a Doctor?
While most skin lumps are harmless, certain characteristics warrant professional medical evaluation. Seek medical attention if a lump grows rapidly, changes color or texture, becomes increasingly painful, or develops an irregular shape. Lumps that feel hard, immovable, or firmly attached to underlying tissue require assessment. Any lump accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever, unexplained weight loss, or fatigue should be evaluated promptly.
Additionally, consult a healthcare provider if multiple lumps appear simultaneously, if a lump interferes with daily activities, or if you have a family history of skin cancer or other malignancies. Trust your instincts – if something feels different or concerning about a lump, professional evaluation provides peace of mind and ensures appropriate care.
What to Expect During a Medical Check
During a medical examination for skin lumps, healthcare providers typically begin with a thorough visual inspection and physical examination. They’ll assess the lump’s size, consistency, mobility, and relationship to surrounding tissues. The provider will also review your medical history, including any family history of skin conditions or cancers, and discuss when you first noticed the lump and any changes you’ve observed.
Depending on the initial assessment, additional tests may be recommended. These might include imaging studies like ultrasound to evaluate the lump’s internal structure, or in some cases, a biopsy to obtain tissue samples for laboratory analysis. Blood tests may be ordered if infection or systemic conditions are suspected. Most evaluations are straightforward and can be completed during a single office visit.
How to Care for Your Skin and Prevent Lumps
Maintaining healthy skin practices can help reduce the likelihood of developing certain types of lumps. Regular cleansing with gentle, non-comedogenic products helps prevent pore blockages that can lead to cysts. Moisturizing keeps skin supple and may reduce the risk of ingrown hairs and irritation-related lumps. Avoiding tight clothing and using proper shaving techniques can minimize trauma-related lump formation.
Protecting skin from excessive sun exposure through sunscreen use and protective clothing helps maintain overall skin health. Regular self-examinations allow for early detection of any new or changing lumps. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with proper nutrition, adequate hydration, and regular exercise supports overall skin health and immune function, potentially reducing the risk of infection-related lumps.
Most skin lumps resolve on their own or remain stable and harmless throughout life. However, staying informed about their characteristics and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers ensures that any concerning changes receive appropriate attention. Remember that early evaluation of suspicious lumps leads to better outcomes when treatment is necessary, making awareness and proactive healthcare essential components of skin health maintenance.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.