Scalp Psoriasis Explained: Symptoms, Causes, and Relief Options
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes red, scaly patches on the scalp, often accompanied by itching and discomfort. Understanding the symptoms, identifying triggers, and exploring available treatment options can help individuals manage flare-ups more effectively. This guide provides comprehensive information on recognizing scalp psoriasis, understanding what causes outbreaks, and discovering relief strategies that work.
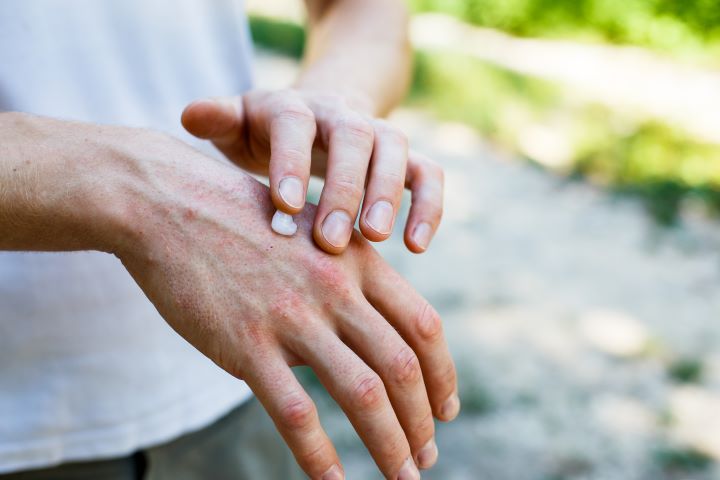

Scalp psoriasis affects millions of people worldwide, presenting unique challenges due to its visibility and the discomfort it causes. This chronic skin condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly accelerates skin cell production, leading to buildup on the scalp. While it shares some characteristics with dandruff, scalp psoriasis is distinct in its appearance and requires specific management approaches. Learning about this condition empowers individuals to seek appropriate care and find relief.
What Are the Common Symptoms of Scalp Psoriasis?
Recognizing scalp psoriasis begins with understanding its characteristic symptoms. The condition typically presents as raised, reddish patches covered with silvery-white scales. These patches can appear anywhere on the scalp, extending beyond the hairline to the forehead, neck, and behind the ears. Unlike simple dandruff, the scales are thicker and often have a powdery appearance.
Itching is one of the most common and bothersome symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. Some individuals experience soreness or a burning sensation in affected areas. In more severe cases, the scalp may bleed when scales are removed or scratched. Hair loss can occur, though it is usually temporary and related to scratching or the inflammation itself rather than the psoriasis directly damaging hair follicles. The scalp may feel dry and tight, and the visible nature of the condition can significantly impact self-esteem and quality of life.
What Triggers Scalp Psoriasis Flare-Ups?
Understanding what triggers flare-ups is essential for managing scalp psoriasis effectively. Stress is one of the most commonly reported triggers, as it can weaken the immune system and exacerbate autoimmune responses. Environmental factors such as cold, dry weather often worsen symptoms, while humidity and sunlight may provide relief for some individuals.
Infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections, can trigger or worsen psoriasis outbreaks. Certain medications, including lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarial drugs, have been associated with flare-ups. Skin injuries to the scalp, known as the Koebner phenomenon, can cause new psoriasis patches to form at the injury site. This includes scratches, cuts, or even harsh hair treatments.
Lifestyle factors also play a role. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to increased psoriasis severity. Hormonal changes, such as those during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can influence symptom intensity. Identifying personal triggers through careful observation helps individuals take preventive measures and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
What Are the Most Effective Treatment Options for Scalp Psoriasis?
Treatment approaches for scalp psoriasis vary based on severity and individual response. Topical treatments are typically the first line of defense. Medicated shampoos containing coal tar, salicylic acid, or selenium sulfide help reduce scaling and inflammation. These are available over-the-counter and can be effective for mild to moderate cases.
Corticosteroid solutions, foams, and oils are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow skin cell turnover. Vitamin D analogues, such as calcipotriene, work by normalizing skin cell production and are often combined with corticosteroids for enhanced effectiveness. Topical retinoids may also be recommended, though they require careful application to avoid irritation.
For moderate to severe cases, phototherapy using ultraviolet light can be beneficial. This treatment slows skin cell growth and reduces inflammation. Systemic medications, including oral or injected drugs that work throughout the body, may be necessary when topical treatments prove insufficient. Biologic drugs target specific parts of the immune system and have shown significant success in managing severe psoriasis. These treatments require medical supervision and regular monitoring.
How Can You Manage Scalp Psoriasis Flare-Ups at Home?
Home management strategies complement medical treatments and can significantly improve comfort during flare-ups. Gentle hair care is crucial. Using lukewarm water instead of hot water prevents further irritation, and avoiding harsh shampoos or styling products reduces scalp stress. Limiting the use of heat styling tools also helps.
Moisturizing the scalp regularly with oils such as coconut, olive, or mineral oil can soften scales and reduce itching. Applying oil before bedtime and covering the head with a shower cap allows for deeper penetration. Gently removing scales with a soft brush or comb after softening them prevents damage to the scalp.
Stress management techniques, including meditation, yoga, or regular exercise, can reduce flare-up frequency. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, supports overall skin health. Staying hydrated and getting adequate sleep also contribute to symptom management. Avoiding known triggers and maintaining a consistent hair care routine create a stable environment for the scalp to heal.
Which Scalp Psoriasis Treatments Are Most Commonly Prescribed by Dermatologists?
Dermatologists typically prescribe treatments based on the severity of the condition and patient response to initial therapies. Topical corticosteroids remain the most frequently prescribed treatment due to their effectiveness in reducing inflammation and controlling symptoms quickly. These are available in various strengths, with stronger formulations reserved for severe cases.
Calcipotriene, a synthetic form of vitamin D, is another commonly prescribed topical treatment. It is often used in combination with corticosteroids to maximize benefits while minimizing side effects. For patients who do not respond adequately to topical treatments, dermatologists may recommend phototherapy sessions, which involve controlled exposure to ultraviolet light.
Systemic treatments, including methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin, are prescribed for severe or widespread psoriasis. These medications work throughout the body to suppress the immune response. Biologic medications, such as adalimumab, etanercept, and ustekinumab, have become increasingly popular for their targeted approach and effectiveness in managing moderate to severe cases. Dermatologists carefully evaluate each patient to determine the most appropriate treatment plan, often adjusting therapies based on response and side effects.
Conclusion
Scalp psoriasis is a manageable condition with the right combination of medical treatment, home care, and lifestyle adjustments. Recognizing symptoms early, understanding personal triggers, and working closely with healthcare professionals enable individuals to control flare-ups and maintain scalp health. While there is no cure, numerous effective treatment options provide relief and improve quality of life. Staying informed and proactive in managing this condition empowers individuals to live comfortably despite the challenges scalp psoriasis presents.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.