Scalp Psoriasis Explained: What Causes It and How to Treat It
Dealing with constant itching, flaking, or thick patches on your scalp? It could be more than dandruff—it might be scalp psoriasis. This common autoimmune condition can lead to irritation, embarrassment, and even hair thinning if ignored. In this guide, you'll discover what causes it, how to spot early symptoms, and which soothing treatments actually work. Whether you're newly diagnosed or tired of recurring flare-ups, here’s your path to a calmer, healthier scalp.
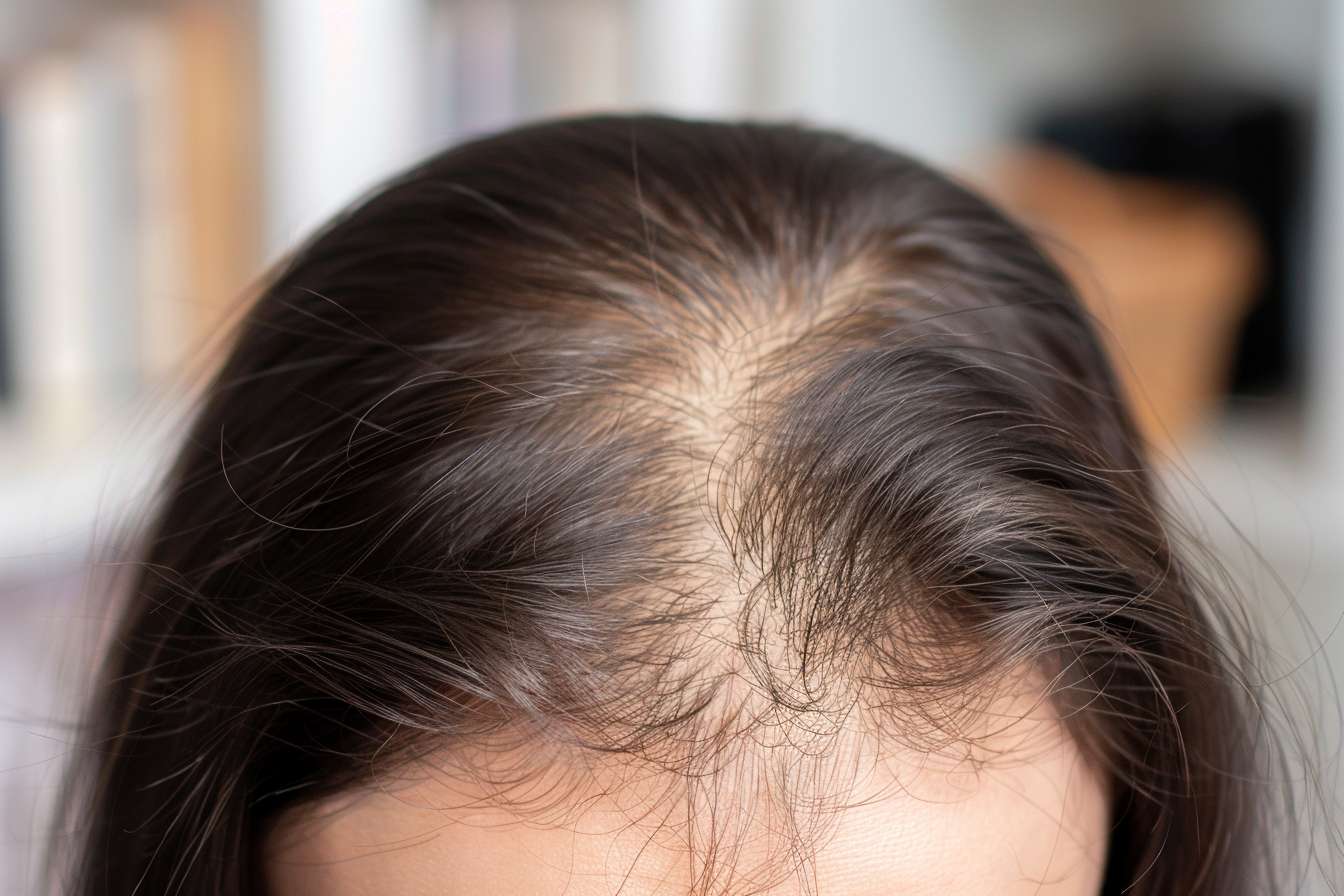
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that manifests as raised, red patches covered with silvery-white scales on the scalp. Unlike dandruff or other scalp conditions, psoriasis involves an overactive immune system that causes skin cells to multiply rapidly, creating thick, scaly buildup. The condition can range from mild scaling to severe, thick plaques that extend beyond the hairline onto the forehead, neck, and ears.
This autoimmune disorder affects approximately 2-3% of the population, with many experiencing their first symptoms during young adulthood. The condition tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component, though environmental factors often trigger initial outbreaks or flare-ups.
What Are the Visual Signs Found in Psoriasis Pictures
Recognizing scalp psoriasis requires understanding its distinctive visual characteristics. The condition typically appears as well-defined, raised patches with thick, silvery-white scales that differ significantly from regular dandruff. These plaques often have clearly marked borders and can vary in size from small spots to large areas covering significant portions of the scalp.
The affected areas usually display a characteristic salmon-pink or red coloration beneath the scales. Unlike seborrheic dermatitis, which tends to be yellowish and greasy, psoriatic scales appear dry and silvery. Hair loss may occur in severe cases, though it’s typically temporary and hair usually regrows once the condition is controlled.
Understanding Pictures of Plaque Psoriasis on the Scalp
Plaque psoriasis represents the most common form of scalp psoriasis, characterized by thick, raised lesions covered with scales. These plaques can appear anywhere on the scalp but commonly develop along the hairline, behind the ears, and on the back of the neck. The thickness of these plaques distinguishes them from other scalp conditions.
Photographic documentation often shows how plaque psoriasis creates distinct, coin-shaped lesions that can merge to form larger affected areas. The scales may appear loose and flaky or tightly adherent to the underlying skin. In darker skin tones, the plaques may appear more purple or darker red, while the scaling remains characteristically silvery-white.
Why Scalp Psoriasis Picking Worsens the Condition
Picking at psoriatic scales creates a cycle that significantly worsens the condition through a phenomenon called the Koebner response. This reaction causes new psoriatic lesions to develop at sites of skin trauma or irritation. When individuals scratch or pick at scales, they create micro-injuries that trigger the immune system to produce more inflammation and scaling.
The picking behavior also increases the risk of secondary bacterial infections, which can complicate treatment and healing. Additionally, aggressive scratching can cause temporary hair loss and scarring. The itching sensation that drives picking behavior often intensifies when the skin becomes more irritated, creating a difficult cycle to break without proper intervention and treatment strategies.
Root Causes and Triggers of Scalp Psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis results from a complex interaction between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. The condition involves T-cells, a type of white blood cell, mistakenly attacking healthy skin cells, causing rapid cell turnover and inflammation. Family history plays a significant role, with individuals having a parent or sibling with psoriasis facing increased risk.
Common triggers include stress, infections (particularly streptococcal throat infections), certain medications, weather changes, and skin injuries. Hormonal changes, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can also precipitate flare-ups. Identifying personal triggers helps in developing effective management strategies and preventing severe outbreaks.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Effective scalp psoriasis treatment typically involves a combination of topical therapies, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes systemic treatments. Topical corticosteroids remain the first-line treatment, available in various formulations including shampoos, foams, and solutions designed specifically for scalp application.
Medicated shampoos containing coal tar, salicylic acid, or ketoconazole can help remove scales and reduce inflammation. Vitamin D analogs like calcipotriene offer effective treatment with fewer side effects than long-term steroid use. For severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe systemic medications including methotrexate, biologics, or cyclosporine.
| Treatment Type | Provider/Brand | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Prescription Topical Steroids | Dermatologist/Pharmacy | $50-200 per month |
| Medicated Shampoos | Over-the-counter | $15-40 per bottle |
| Vitamin D Analogs | Prescription | $100-300 per month |
| Biologic Medications | Specialty Pharmacy | $3,000-6,000 per month |
| Phototherapy Sessions | Dermatology Clinic | $75-150 per session |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Successful management also involves gentle hair care practices, stress reduction techniques, and maintaining overall skin health. Regular follow-ups with dermatologists ensure treatment effectiveness and allow for adjustments based on response and side effects. Many patients find that combining medical treatments with lifestyle modifications provides the best long-term outcomes for controlling scalp psoriasis symptoms.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.