Solar Panels in the United States: Your 2025 Guide to Benefits, and Technology
As we step into 2025, solar energy continues to play a pivotal role in the United States' renewable energy landscape. This guide explores the latest developments in solar panel technology, the expanding adoption of solar energy across the country, and the potential benefits for property owners. Whether you're considering solar panels for your home or business, or simply curious about this growing energy source, this comprehensive overview will shed light on the current state of solar power in the U.S.
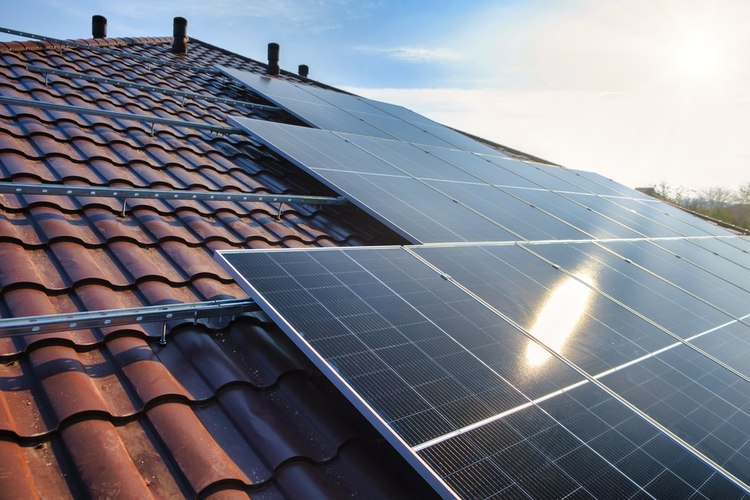

Why is Solar Energy Expanding in the U.S.?
The growth of solar energy in the United States can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, technological advancements have significantly improved the efficiency and durability of solar panels, making them more attractive to consumers. Secondly, federal and state incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, have made solar installations more financially accessible. Additionally, increased awareness of climate change and the desire for energy independence have driven many Americans to consider solar as a viable alternative to traditional power sources.
The declining costs of solar panel production and installation have also contributed to the industry’s expansion. As economies of scale come into play, solar energy is becoming increasingly competitive with conventional electricity sources in many parts of the country. This cost-effectiveness, combined with the long-term savings on electricity bills, has made solar an appealing option for both residential and commercial property owners.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
Solar panels harness the power of sunlight to generate electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. Each panel consists of multiple photovoltaic cells, typically made from silicon, which absorb photons from sunlight. When photons strike these cells, they excite electrons, causing them to flow and generate an electric current.
This direct current (DC) electricity is then converted to alternating current (AC) by an inverter, making it compatible with the electrical grid and household appliances. Any excess energy produced can be stored in batteries for later use or fed back into the grid, often resulting in credits on the owner’s electricity bill through net metering programs.
Modern solar panel systems are equipped with sophisticated monitoring technology, allowing users to track their energy production and consumption in real-time. This data helps optimize energy usage and provides valuable insights into the system’s performance over time.
Signs Your Property May Benefit from Solar
Several factors can indicate whether your property is well-suited for solar panel installation:
-
Ample sunlight exposure: Properties with unobstructed southern-facing roofs or open land areas tend to receive more direct sunlight throughout the day, maximizing solar energy production.
-
High electricity bills: If you consistently face high energy costs, solar panels could provide significant long-term savings.
-
Suitable roof condition: A roof in good condition with adequate space and appropriate pitch can easily accommodate solar panels.
-
Local incentives: Some regions offer additional incentives for solar adoption, making the investment even more attractive.
-
Long-term occupancy plans: If you intend to stay in your property for several years, you’re more likely to reap the full benefits of your solar investment.
-
Environmental concerns: For those prioritizing reduced carbon footprints, solar energy offers a clean, renewable alternative to fossil fuels.
Average Costs of Solar Panels in the U.S. (2025)
The cost of solar panel systems can vary widely depending on factors such as location, system size, and equipment quality. As of 2025, the average cost of solar panel installation in the United States ranges from $2.50 to $3.50 per watt before incentives. For a typical residential system size of 6 kilowatts (kW), this translates to a total cost between $15,000 and $21,000.
Here’s a comparison of average costs for different system sizes:
| System Size (kW) | Average Cost Range (Before Incentives) |
|---|---|
| 4 kW | $10,000 - $14,000 |
| 6 kW | $15,000 - $21,000 |
| 8 kW | $20,000 - $28,000 |
| 10 kW | $25,000 - $35,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
It’s important to note that these figures represent the upfront costs before applying any federal or state incentives. The federal solar investment tax credit (ITC) allows homeowners to deduct 30% of the cost of installing a solar energy system from their federal taxes, significantly reducing the overall expense. Additional state and local incentives may further lower the net cost of going solar.
While the initial investment may seem substantial, many homeowners find that the long-term savings on electricity bills, combined with increased property values, make solar panels a worthwhile investment. The payback period for a solar panel system in the U.S. typically ranges from 7 to 10 years, after which the system continues to generate free electricity for its expected lifespan of 25-30 years.
As solar technology continues to advance and manufacturing processes become more efficient, it’s likely that the cost of solar panels will continue to decrease, making this clean energy option even more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
In conclusion, solar panels represent a growing trend in the United States’ energy landscape. With improving technology, expanding adoption, and potential financial benefits, solar energy is poised to play an increasingly significant role in powering American homes and businesses. As we move further into 2025 and beyond, the solar industry’s continued growth and innovation promise to make clean, renewable energy more accessible and affordable for all.