Custom Manufacturing Solutions for Every Industry Need
Modern manufacturing is experiencing a revolutionary transformation through advanced three-dimensional printing technologies. These sophisticated systems enable businesses across various sectors to create customized products, prototypes, and components with unprecedented precision and efficiency. From aerospace components to medical devices, 3D printing technology offers manufacturers the flexibility to produce complex geometries and personalized solutions that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. This innovative approach to production is fundamentally changing how companies approach design, testing, and manufacturing processes.
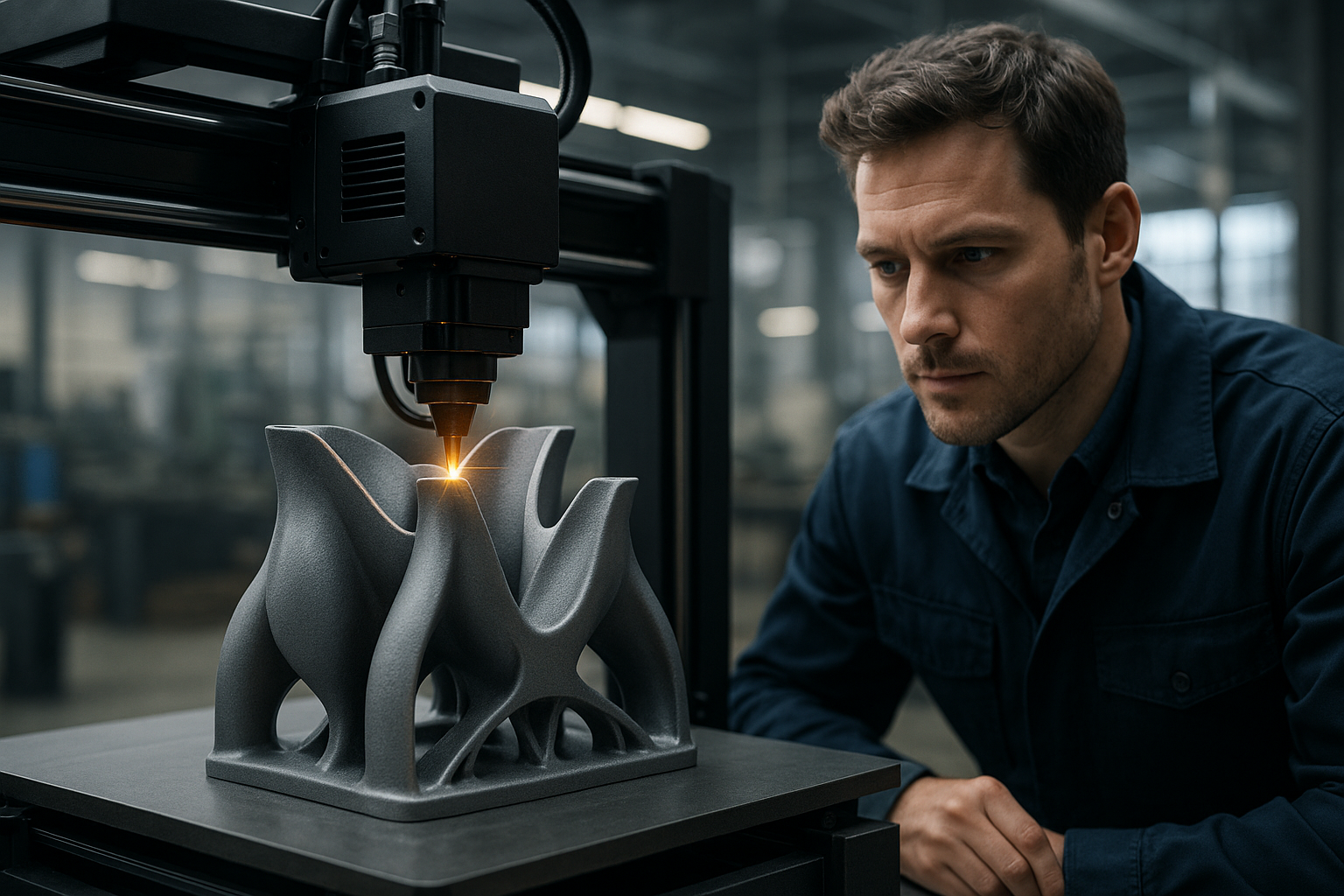

How Technology Evolution Transforms Manufacturing Possibilities
As the technology evolves, 3D printers continue to blur the boundary between imagination and reality. Advanced additive manufacturing systems now support a wide range of materials, from basic plastics to high-performance metals, ceramics, and composite materials. These technological improvements have expanded the applications beyond simple prototyping to full-scale production runs for specialized components.
Modern 3D printing technologies utilize various methods including fused deposition modeling, stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and direct metal laser sintering. Each technique offers unique advantages for specific applications, allowing manufacturers to select the most appropriate method based on material requirements, precision needs, and production volumes.
Achieving Perfect Balance of Precision, Customization, and Speed
Precision, customization, and speed come together to redefine what’s possible for makers and professionals alike. Contemporary 3D printing systems achieve layer resolutions as fine as 25 microns, enabling the production of intricate details and smooth surface finishes that rival traditional manufacturing methods.
Customization capabilities allow manufacturers to produce unique items without the need for expensive tooling or molds. This flexibility proves particularly valuable in industries such as healthcare, where patient-specific medical devices and implants require individual customization. The speed advantages become apparent in rapid iteration cycles, where design modifications can be implemented and tested within hours rather than weeks.
Revolutionizing Design, Testing, and Production Workflows
From rapid prototyping to personalized products, 3D printing is reshaping how we design, test, and build. Traditional product development cycles that once required months can now be compressed into weeks or days. Engineers can quickly produce functional prototypes, test designs under real-world conditions, and make necessary adjustments before committing to large-scale production.
This technology enables complex internal geometries, lightweight structures, and consolidated assemblies that would be impossible or extremely expensive to produce using conventional manufacturing methods. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods leverage these capabilities to create innovative products with improved performance characteristics.
Industrial Applications Across Diverse Sectors
Various industries have adopted 3D printing technologies for different applications. In aerospace, companies produce lightweight brackets, air ducts, and even engine components using titanium and aluminum alloys. The automotive industry utilizes 3D printing for rapid prototyping, custom tooling, and end-use parts production.
Medical applications include surgical guides, prosthetics, dental implants, and bioprinting research. Architecture and construction sectors employ large-scale 3D printers to create building components and even entire structures using concrete and other construction materials.
Cost Analysis and Equipment Comparison
Understanding the investment requirements helps businesses make informed decisions about 3D printing implementation. Equipment costs vary significantly based on technology type, build volume, and material capabilities.
| Equipment Type | Price Range | Build Volume | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop FDM Printers | $200 - $5,000 | Small to Medium | Prototyping, Education |
| Professional SLA Systems | $3,000 - $50,000 | Medium | High-detail prototypes |
| Industrial SLS Machines | $100,000 - $500,000 | Large | Production parts |
| Metal 3D Printers | $500,000 - $2,000,000 | Variable | Aerospace, Medical |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Operational costs include materials, maintenance, and skilled operator training. Material costs range from $20-50 per kilogram for standard plastics to $300-800 per kilogram for specialized metals and ceramics.
Future Developments and Market Trends
The 3D printing industry continues advancing with developments in multi-material printing, increased printing speeds, and expanded material options. Emerging technologies include continuous liquid interface production, which dramatically reduces printing times, and hybrid manufacturing systems that combine additive and subtractive processes.
Sustainability initiatives focus on recyclable materials and reduced waste production. As technology matures and costs decrease, adoption rates across small and medium enterprises continue growing, democratizing access to advanced manufacturing capabilities.
These manufacturing solutions represent a fundamental shift toward more flexible, efficient, and customizable production methods. Organizations that embrace these technologies position themselves to respond quickly to market demands while reducing traditional manufacturing constraints and limitations.